In the fast-paced and competitive business landscape of the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) countries, organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of prioritizing employee health and wellness. With diverse work environments, cultural norms, and demanding workloads, fostering a culture of well-being is essential for promoting employee satisfaction, productivity, and overall organizational success. In this blog, we’ll explore the significance of health and wellness programs for employees in the GCC countries, discuss the benefits they offer, and provide strategies for implementing effective programs tailored to the region’s unique needs.
The Importance of Health and Wellness Programs in GCC Countries:
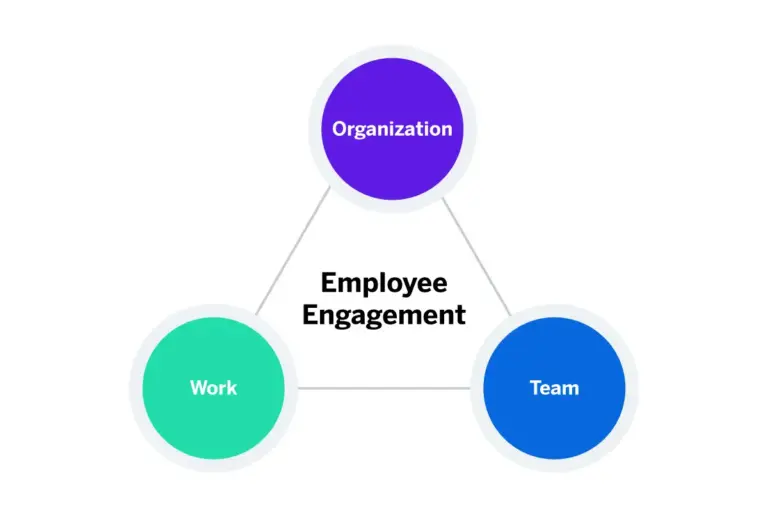
- Improved Employee Well-being: health and wellness programs for employees promote physical, mental, and emotional well-being among employees, reducing stress, burnout, and absenteeism, and enhancing overall quality of life.
- Increased Productivity and Performance: Healthy and happy employees are more engaged, motivated, and productive, leading to improved performance and organizational success in the competitive GCC market.
- Enhanced Employee Satisfaction and Retention: Offering health and wellness programs demonstrates a commitment to employee satisfaction and well-being, leading to higher retention rates and increased loyalty among employees.
- Cost Savings: Investing in employee health and wellness programs for employees can result in cost savings for organizations by reducing healthcare expenses, lowering absenteeism, and improving employee morale and productivity.
- Positive Organizational Culture: Health and wellness programs contribute to creating a positive organizational culture that values employees’ holistic well-being, fosters a supportive work environment, and promotes work-life balance.
Key Components of Health and Wellness Programs for GCC Employees:
- Physical Health Initiatives: Offer fitness classes, gym memberships, health screenings, and nutrition programs to encourage employees to adopt healthy lifestyle habits and improve their physical fitness.
- Mental Health Support: Provide access to counseling services, stress management workshops, and mindfulness training to support employees’ mental and emotional well-being and reduce workplace stress.
- Work-Life Balance Policies: Implement flexible work arrangements, telecommuting options, and paid time off policies to help employees achieve a healthy balance between their work and personal lives.
- Health Education and Awareness: Offer workshops, seminars, and webinars on topics such as nutrition, exercise, mental health, and stress management to educate employees and empower them to make informed health choices.
- Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Establish EAPs to provide confidential support and resources to employees facing personal or work-related challenges, including financial counseling, legal assistance, and family support services.
Strategies for Implementing Health and Wellness Programs in GCC Organizations:
- Cultural Sensitivity: Tailor health and wellness programs to align with the cultural norms, preferences, and religious practices of employees in the GCC countries, ensuring inclusivity and respect for diversity.
- Leadership Support: Gain buy-in and support from organizational leaders and management to prioritize employee health and wellness programs for employees initiatives and allocate resources for program implementation and promotion.
- Employee Engagement: Involve employees in the design, planning, and evaluation of health and wellness programs to ensure they meet their needs and preferences and encourage active participation and engagement.
- Communication and Promotion: Use multiple communication channels, such as email, intranet, posters, and workshops, to raise awareness about health and wellness programs, educate employees about their benefits, and encourage participation.
- Evaluation and Continuous Improvement: Regularly assess the effectiveness of health and wellness programs through employee feedback, surveys, and metrics such as participation rates, health outcomes, and satisfaction levels, and make adjustments as needed to ensure ongoing success.