In a world where efficiency and quality are paramount, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline their processes and minimize defects. Enter Lean Six Sigma—a powerful methodology that has become synonymous with operational excellence. In this blog, we will delve into the world of Lean Six Sigma, uncovering its principles, benefits, and how it can revolutionize your organization.
Chapter 1: Understanding Lean Six Sigma
What is Lean Six Sigma?
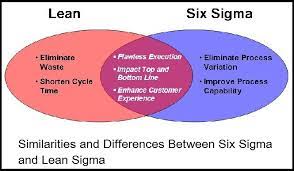
Lean Six Sigma is a blend of two powerful process improvement methodologies—Lean and Six Sigma. Lean focuses on eliminating waste and increasing process efficiency, while Six Sigma is dedicated to reducing defects and variations. Combining these approaches results in a holistic methodology that drives both efficiency and quality.
Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
- Customer-Centric: Prioritizes meeting customer needs and expectations.
- Data-Driven: Relies on data and statistical analysis for decision-making.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourages ongoing efforts to enhance processes.
- Team Collaboration: Involves cross-functional teams to solve problems.
Chapter 2: The DMAIC Process in Lean Six Sigma
Define Phase
In this initial phase, you define the problem, project goals, and customer requirements. Clarity in objectives is crucial to ensure the project’s success.
Measure Phase
This phase involves collecting data to understand the current state of the process. Metrics are analyzed to identify areas of improvement.
Analyze Phase
With data in hand, you dig deeper to uncover the root causes of defects or inefficiencies. Tools like Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts aid in this phase.
Improve Phase
Here, you brainstorm solutions and implement changes to the process. The goal is to optimize it for maximum efficiency and quality.
Control Phase
In the final phase, you establish controls to sustain improvements over time. This includes monitoring the process and implementing preventive measures.
Chapter 3: The Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
Enhanced Efficiency
Lean Six Sigma identifies and eliminates wasteful steps in processes, leading to significant efficiency gains.
Improved Quality
By reducing defects and variations, organizations can deliver higher-quality products and services, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Cost Reduction
Efficiency improvements often lead to cost savings, making Lean Six Sigma a valuable tool for financial success.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Lean Six Sigma relies on data, ensuring that decisions are based on facts rather than intuition.
Chapter 4: Real-World Success Stories
Toyota
Toyota is a prime example of the power of Lean principles. The company’s commitment to eliminating waste revolutionized the automotive industry.
General Electric (GE)
GE’s successful adoption of Six Sigma principles, combined with Lean thinking, resulted in substantial cost savings and improved product quality.
Amazon
Amazon’s focus on customer-centric processes and continuous improvement aligns with Lean Six Sigma principles, contributing to its global success.
Chapter 5: Getting Started with Lean Six Sigma
Training and Certification
Invest in training your team or individuals in Lean Six Sigma methodologies to build the necessary skills.
Project Selection
Identify projects that will have a substantial impact on your organization’s goals and customer satisfaction.
Foster a Lean Culture
To ensure long-term success, integrate Lean Six Sigma principles into your organization’s culture, encouraging continuous improvement.